In this Article we are going to learn How to Install Apache2 on Google Cloud Ubuntu 22.04 LTS GCP VM and Setting Up Virtual Hosts on Apache2.
Table of Contents
Step #1:Install Apache2 on Google Cloud Ubuntu 22.04 LTS GCP VM
Update your system package:
sudo apt-get update
Install Apache2 on Google Cloud Ubuntu 22.04 LTS VM
sudo apt-get install apache2
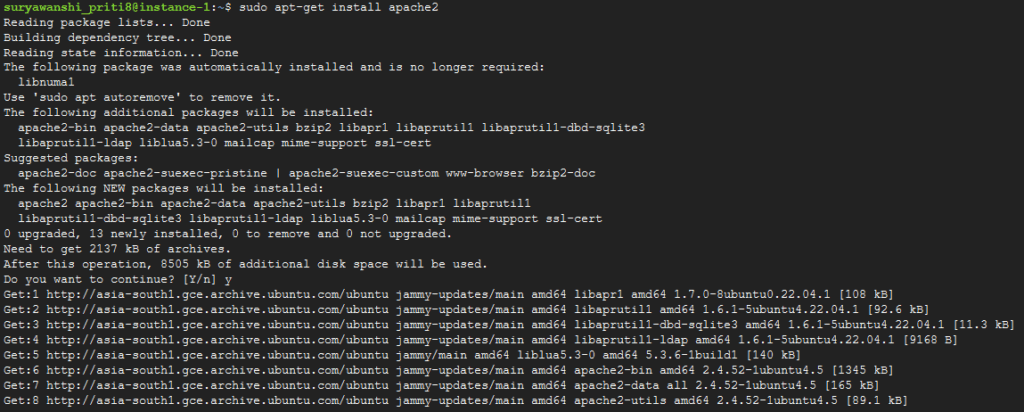
Step #2:Verify Apache2 Installation on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
For Verify Apache was installed correctly, open your favorite web browser and type in the address bar http://external_ip_address
After opening this URL you can see the apache2 default page as in the image below:

Step #3:Configure Firewall in Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
Check the available ufw application profiles:
sudo ufw app list
Let’s enable the most restrictive profile that will still allow the traffic you’ve configured, permitting traffic on port 80:
sudo ufw allow 'Apache'
Verify the change:
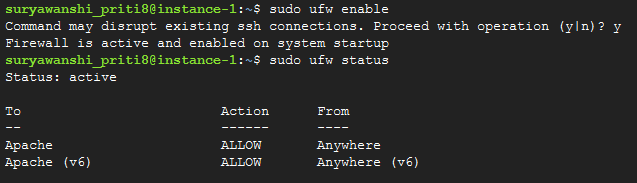
sudo ufw status
If your status is inactive like this:

Then you need to enable first then check the status:
sudo ufw enable
sudo ufw status
Step #4:Managing the Apache2 Process on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
Some basic management commands to manage Apache2 processes on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
To stop your web server, run this command:
sudo systemctl stop apache2
To check the status of your web server, run this command:
sudo systemctl status apache2
To start the web server when it is stopped, run this command:
sudo systemctl start apache2
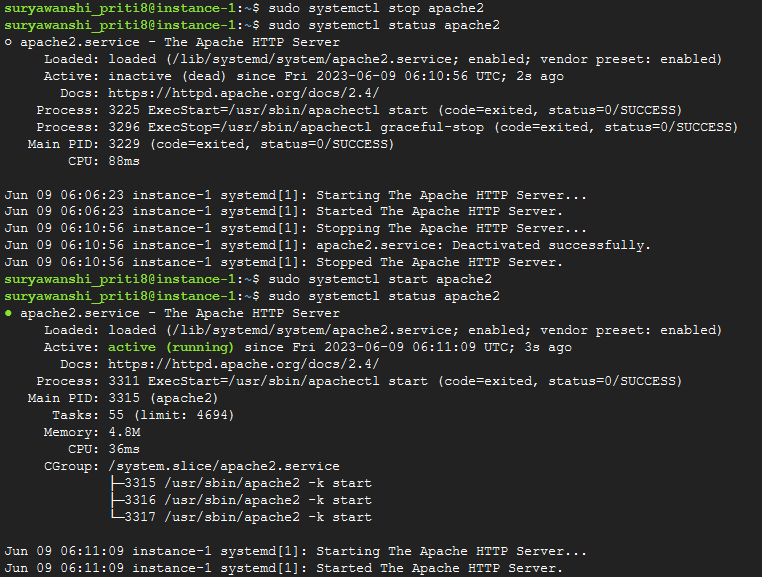
To stop and then start the service again, run this command:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Apache can often reload without dropping connections. To do this, use this command:
sudo systemctl reload apache2
By default, Apache is configured to start automatically when the server boots. If this is not what you want, disable this behavior by typing:
sudo systemctl disable apache2
To re-enable the service to start up at boot, type:
sudo systemctl enable apache2
we have covered Install Apache2 on Google Cloud Ubuntu 22.04 LTS VM.
Step #5:Setting Up Virtual Hosts in Apache2
Create the directory for devopshint as follows:
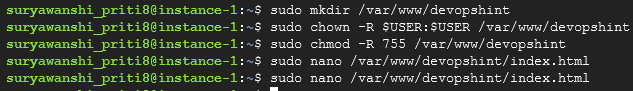
sudo mkdir /var/www/devopshint
Next, assign ownership of the directory to the user you’re currently signed in as with the $USER environment variable:
sudo chown -R $USER:$USER /var/www/devopshint
To ensure that your permissions are correct and allow the owner to read, write, and execute the files while granting only read and execute permissions to groups and others, you can input the following command:
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/devopshint
Next, create a sample index.html page using nano editor:
sudo nano /var/www/devopshint/index.html
Inside, add the following sample HTML:
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to devopshint!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Success! Welcome to devopshint And its working</h1>
</body>
</html>

Save and close the file when you are finished. If you’re using nano, you can do this by pressing CTRL + X, then Y and ENTER.
Make a new one at /etc/apache2/sites-available/devopshint.conf:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/devopshint.conf
Add in the following configuration block, which is similar to the default, but updated for your new directory and domain name:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
ServerName devopshint
ServerAlias www.devopshint
DocumentRoot /var/www/devopshint
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Save and close the file when you are finished.
Now enable the file with the a2ensite tool:
sudo a2ensite devopshint.conf
Disable the default site defined in 000-default.conf:
sudo a2dissite 000-default.conf
Next, test for configuration errors:
sudo apache2ctl configtest
You should receive the following output

Restart Apache to implement your changes:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
You can test this by navigating to http://devopshint, where you will see the changes

Step #6:Apache2 config files and directories
Below are important Apache2 config files and directories
Default Apache Web Content
/var/www/html :When we install Apache2 by default /var/www/html directory gets created and when you access it on browser then content loads from this directory.
Maven2 Server Configuration files
/etc/apache2: This is Apache configuration directory. All of the Apache configuration files reside here.
/etc/apache2/apache2.conf: This is Maven global configuration file when you modify it , it will apply to all content which used Maven.
/etc/apache2/ports.conf: This maven file by default, Apache listens on port 80 and additionally listens on port 443 when a module providing SSL capabilities is enabled.
/etc/apache2/sites-available/: This directory has configuration files for Apache 2 Virtual Hosts. Virtual Hosts allow Apache 2 to be configured for multiple sites that have separate configurations. sites-enabled: like mods-enabled, sites-enabled contains symbolic to the /etc/apache2/sites-available directory: All server block configuration is done in this directory and then enabled by linking to the other directory with the a2ensite command.
/etc/apache2/sites-enabled/: The ../sites-enabled/ folder will include symlinks to the site configuration files located within /etc/maven/sites-available/ directory with the a2ensite.
Maven2 Server Logs
/var/log/apache2/access.log: This is maven2 log file by default, every request to your web server is recorded in this log file unless Apache is configured to do otherwise.
/var/log/apache2/error.log: This is maven2 log file by default, all errors are recorded in this file.
Conclusion:
In this article, We have covered How to Install Apache2 on Google Cloud Ubuntu 22.04 LTS GCP VM and Setting Up Virtual Hosts on Apache2.
Related Articles:
How to Install NGINX on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
Reference: